Transfer data from Postgresql to Google Sheets

Querying for data in a database and editing it in a spreadsheet are simple tasks, and most users should not have problems executing them in everyday work. However, when trying to up our level and use our tools in more effective and connected ways, it might become cumbersome to constantly have to remember all of those architectures with all of their quirks just to accomplish the mundane task of extracting data from PostgreSQL and inserting it into a spreadsheet. Drowning in outdated docs and disorganized notes, MLJAR studio comes to the rescue!
Table of contents
Required libraries
We will need a few packages to connect PostgreSQL and Google Sheets with Python. Here is a list of imports used by MLJAR studio:
import psycopg import os from dotenv import load_dotenv from psycopg import sql import gspread
Get data from PostgreSQL
The most important thing is to keep your database credentials safe. Thankfully MLJAR studio makes managing you secrets easy.
Define a new connection
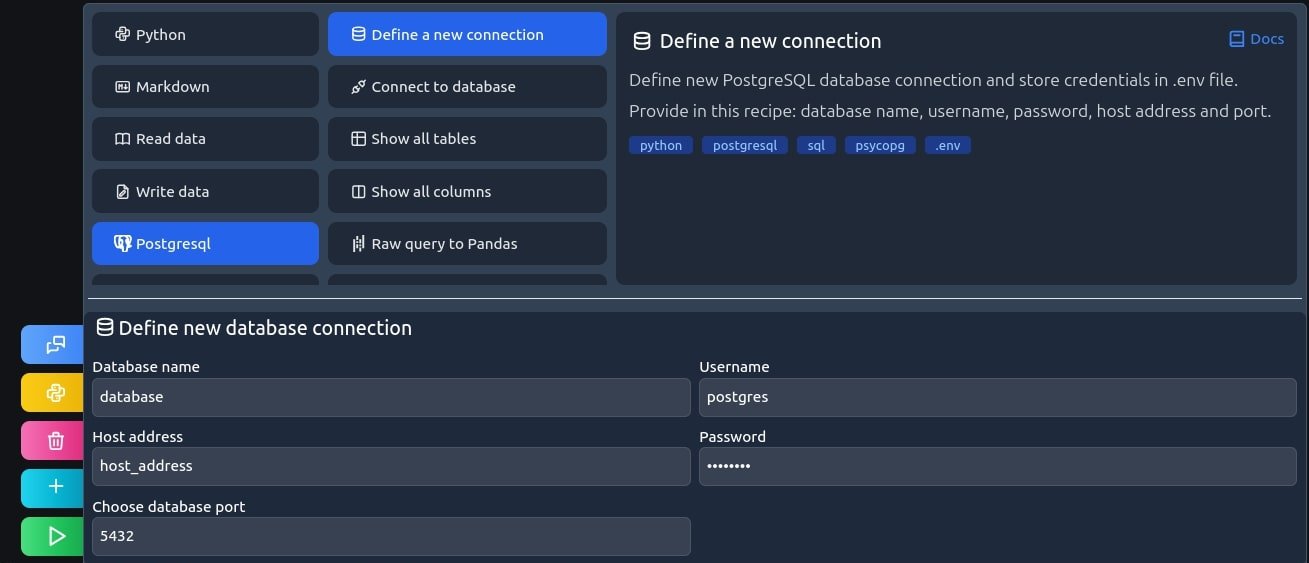
This code recipe saves your secrets in .env file in current working directory, Values in the picture are just a default placeholder in MLJAR Studio, don't share your credentials with anyone you can't 100% trust.
If you want to learn how to manage your data in more of a manual way read the article on how to keep credentials secret in Python Notebook.
Open a new connection
This recipe will open a new database connection using the credentials you defined in the previous recipe. This allows you to open the connection multiple times without needing to reenter the password every time. If you ever want to delete this data, it is stored in a .env file in your current MLJAR studio working directory. If you can't see it, make sure to enable hidden files in your file explorer.
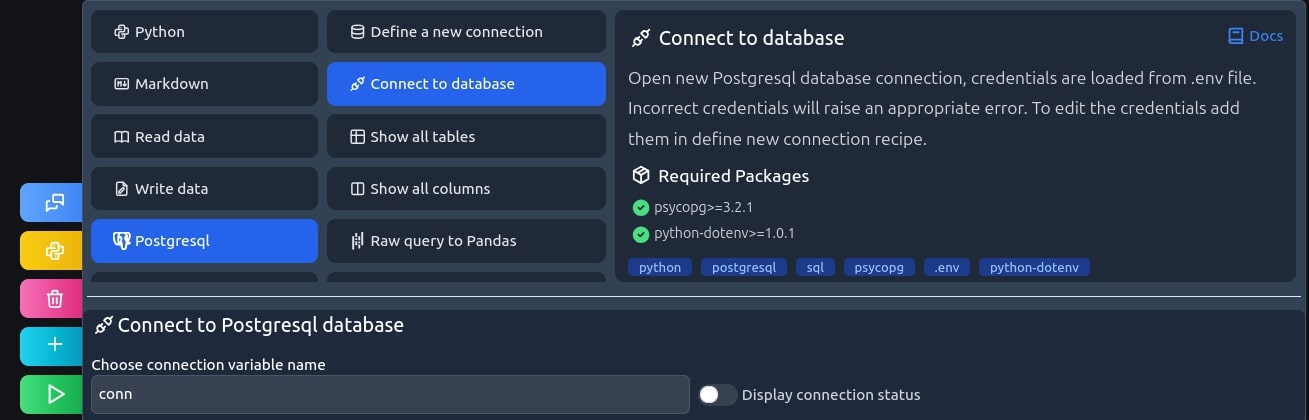
conn = create_new_connection() # display connection status print("Connection status: " + conn.info.status.name)
Now that we are connected, it's time to start using the database.
I will assume that you don't know every table and every column of your database, so I'll show a way to deal with that, using MLJAR studio's PostgreSQL cookbook.
Show all tables
First, let's start with listing our options by using the show all tables recipe.
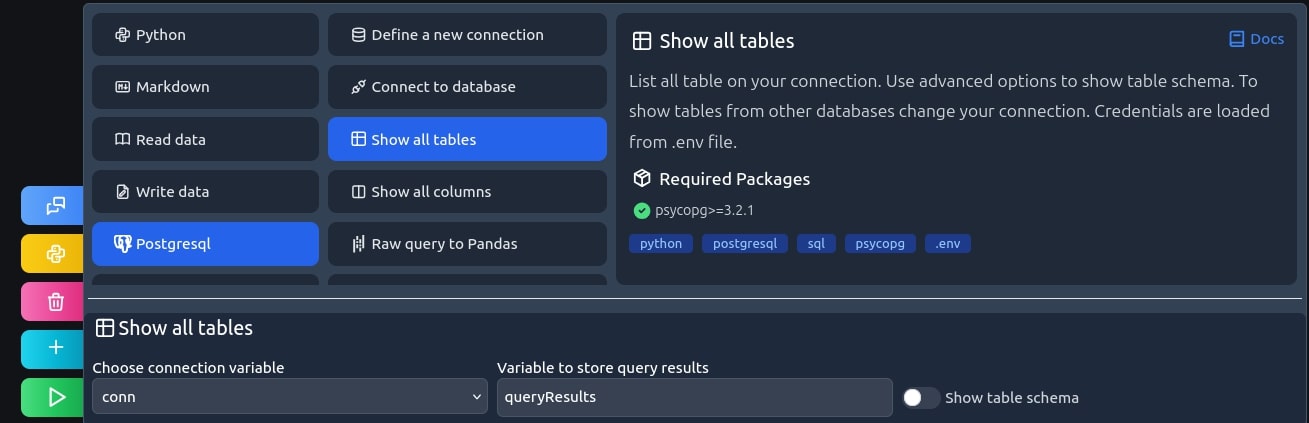
print("Tables:") for table in cursor.fetchall(): print(f"{table}")
This returns a list of available tables in our database.
Output: Tables: ('users',) ('products_backup',) ('products',) ('test',)
Let's focus on the test table in this example.
Show all columns
Similarly, as in the last step, we will list our options, this time using show all columns recipe. It'll list every column of a given table.
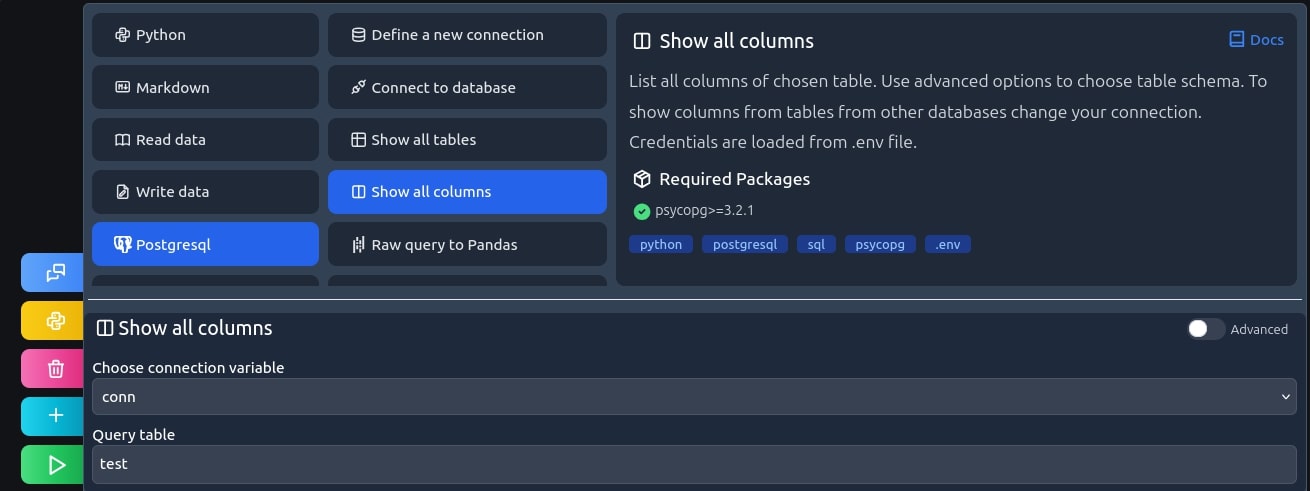
print("Columns of test:") for column in cursor.fetchall(): print(f"{column}")
And the output is as expected a list of every column of our test table.
Output: Columns of test: ('id', 'integer') ('num', 'integer') ('data', 'character varying') ('description', 'character varying')
Great. Now that we know enough about our database, it's time to write a query for our data. To do so, we'll use a select query recipe.
Select the data
Simply specify the table and columns names you want to query for and run it!
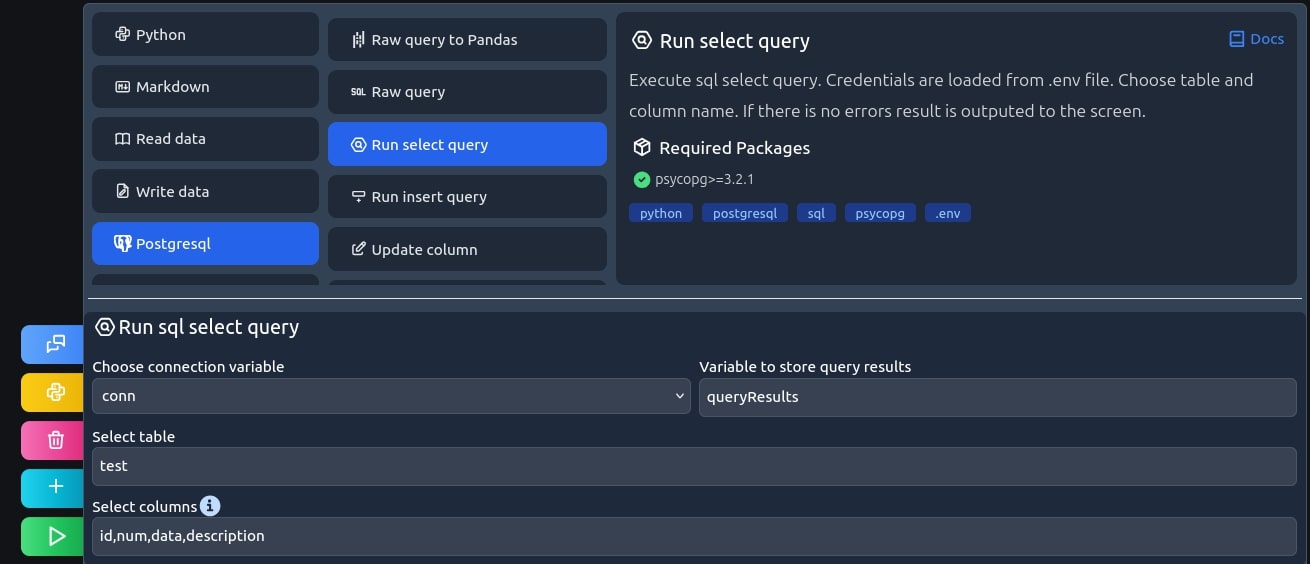
# save query results to a variable queryResults = cursor.fetchall() # print the results for row in queryResults: print(f"{row}")
And the contest of those columns is returned.
Output: (1, 10, 'alice.johnson@example.com', None) (2, 11, 'john.john@example.com', None) (3, 12, 'michael.johnson@example.com', None)
Tip: if you want to select every column without spelling it all out, you can use the * symbol. Give it a try!
Send data to Google sheet
Our data is stored in queryResults variable, we will use it to access the data later. Now we need to connect to Google sheets.
Get a connection
You need to get a Google API key to get one:
- Go to the Google API Console.
- Create a new project.
- Click Enable API. Search for and enable the Google Drive API.
- Create credentials for a Web Server to access Application Data.
- Name the service account and grant it an Editor role.
- Download the JSON file.
- Select the file in MLJAR studio.
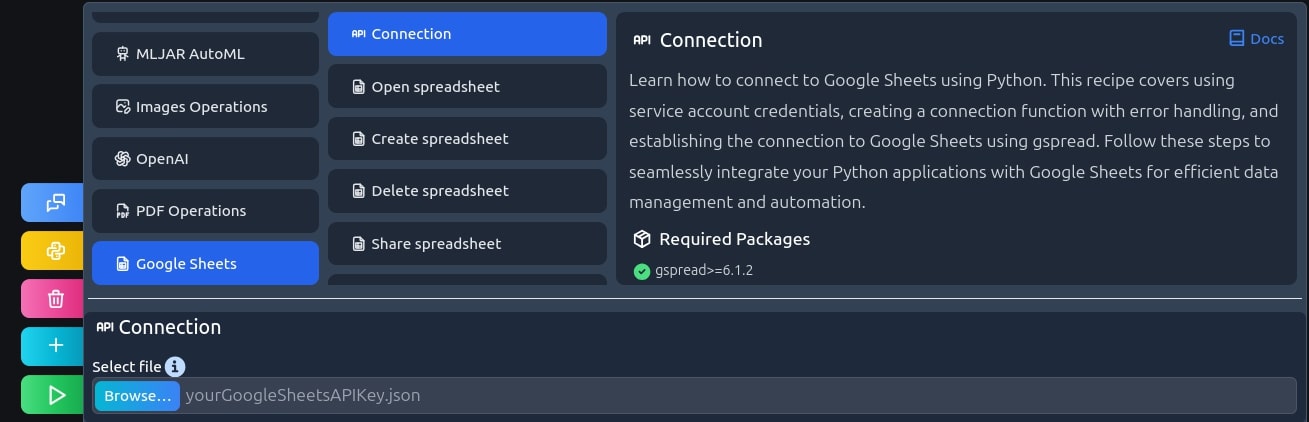
filepath=r"yourGoogleSheetsAPIKey.json" # connect to Google API gc = connection(filepath)
Create a spreadsheet
Now, let's create a new spreadsheet to hold our data and name it test_data_spredsheet.
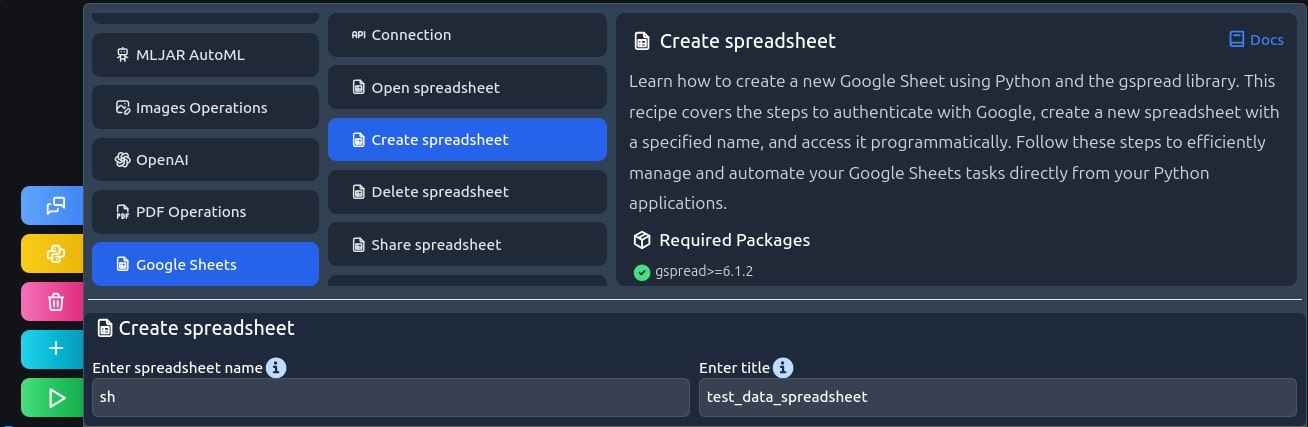
sh = gc.create('test_data_spreadsheet')
Open a worksheet
We need to choose a worksheet, first one will do.
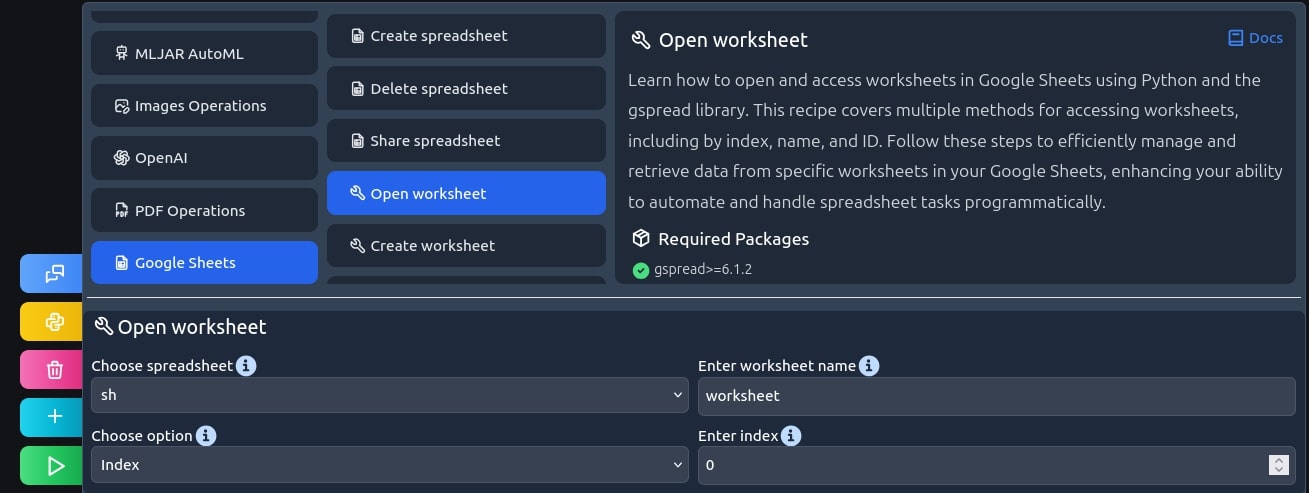
worksheet = sh.get_worksheet(0)
Transfer data
It's time to come back to the queryResults variable from earlier. We need to use it in appending rows recipe to transfer the data to our spreadsheet.
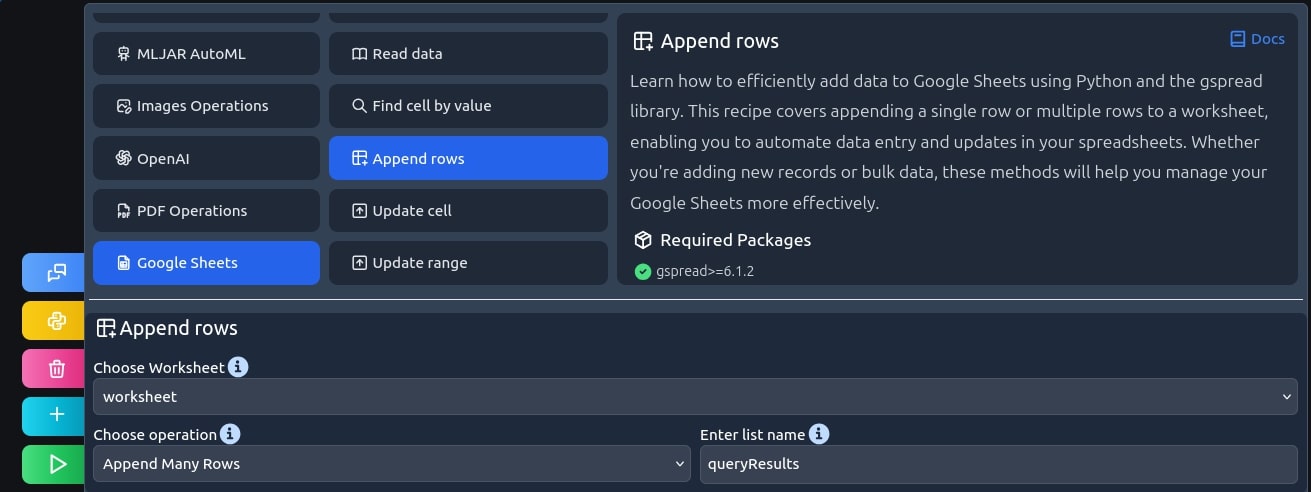
worksheet.append_rows(queryResults)
Output: {'spreadsheetId': 'here a shpread sheet id is dispalyed', 'updates': {'spreadsheetId': here a shpread sheet id is dispalyed', 'updatedRange': 'Sheet1!A1:C3', 'updatedRows': 3, 'updatedColumns': 3, 'updatedCells': 9}}
Output looks good, but just to check if everything went correctly, let's read the spreadsheet data, all inside the editor!
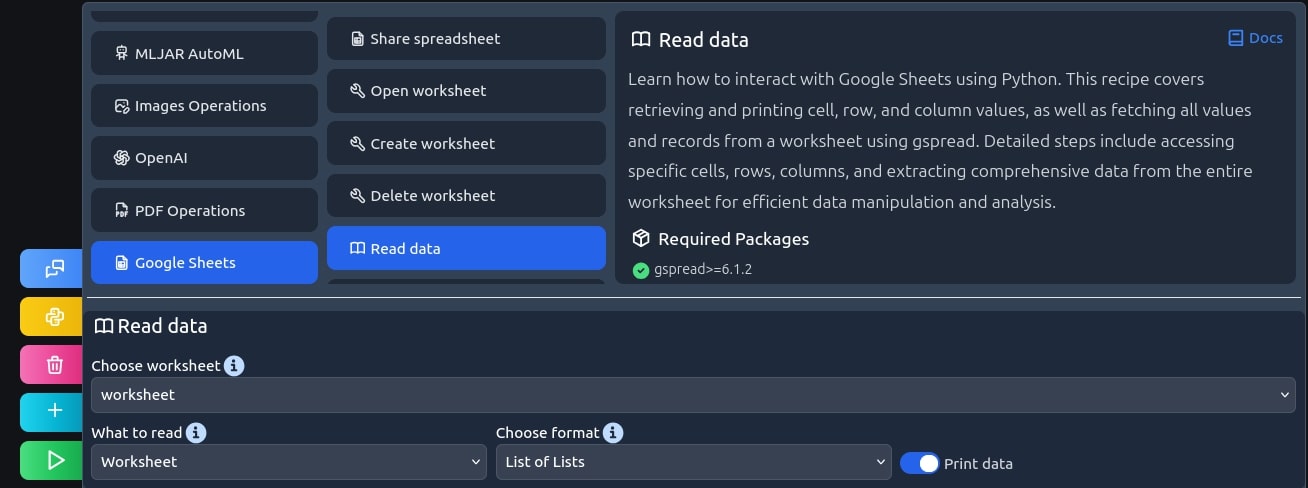
print (worksheet.get_all_values())
Output: [['1', '10', 'alice.johnson@example.com'], ['2', '11', 'john.john@example.com'], ['3', '12', 'michael.johnson@example.com']]
Everything seems correct. I like it!
Share the spreadsheet
If you want to be able to edit the spreadsheet in the Google Sheets web app, you still need to share it. In my opinion, the easiest way is to do it by email. Simply put in your address and wait for a message, follow the steps in the email, and you're all DONE!
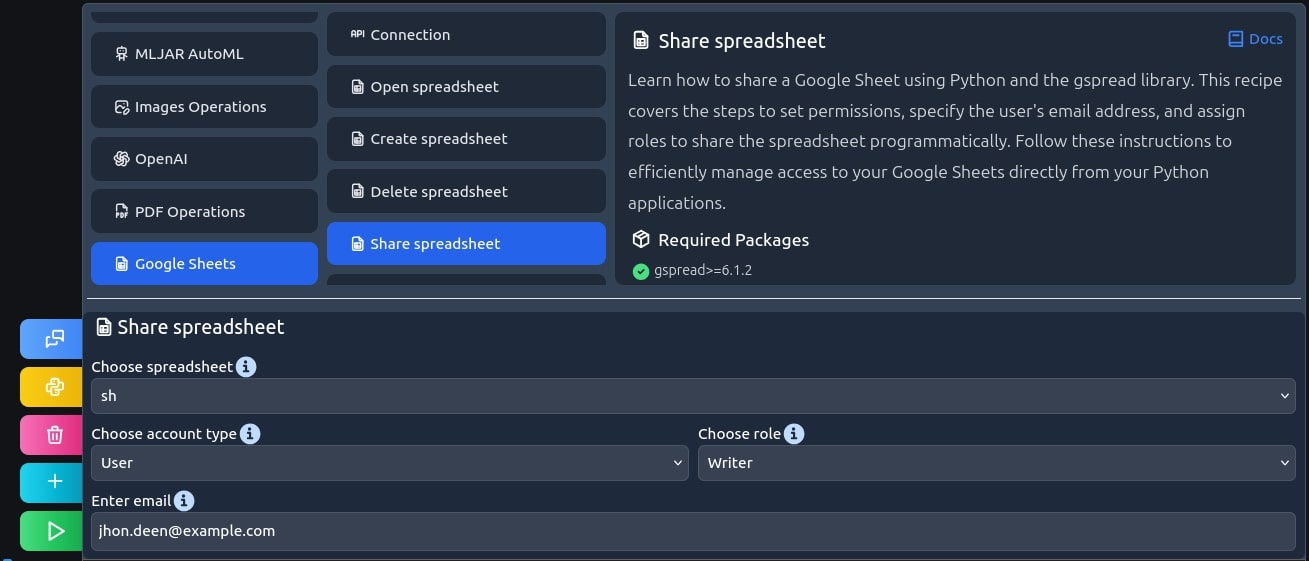
sh.share(email_address='jhon.deen@example.com', perm_type='user', role='reader')
Summary
Congrats! Now, you can convert PostgreSQL data into a Google sheet with MLJAR studio. Share this spreadsheet just like any other.
Run AI for Machine Learning — Fully Local
MLJAR Studio is a private AI Python notebook for data analysis and machine learning. Generate code with AI, run experiments locally, and keep full control over your workflow.
Related Articles
- 3 ways to access credentials in Jupyter Notebook
- How to create Dashboard in Python from PostgreSQL
- How to create Invoice Generator in Python
- ChatGPT can talk with all my Python notebooks
- Create Retrieval-Augmented Generation using OpenAI API
- Machine Learning Algorithm Comparison
- TabNet vs XGBoost
- 4 Effective Ways to Visualize LightGBM Trees
- 4 Effective Ways to Visualize Random Forest
- 4 Effective Ways to Visualize XGBoost Trees